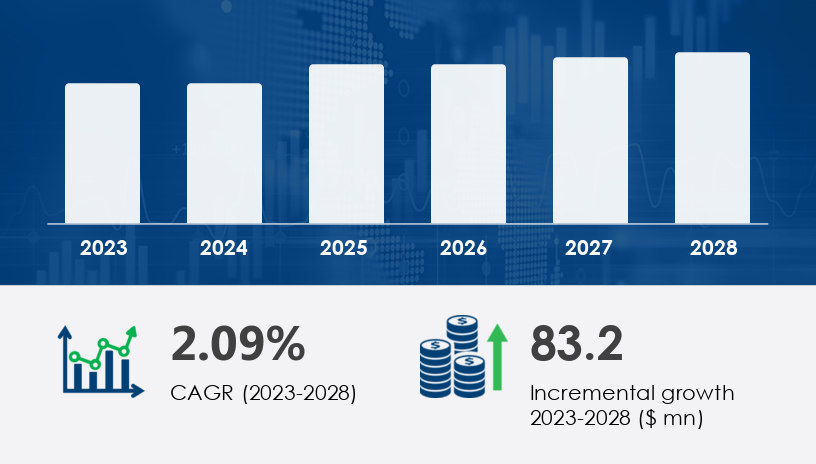
The global gear hobbing machines market is poised for steady expansion, with projections indicating an increase of USD 83.2 million between 2024 and 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.09%. This growth trajectory is underpinned by advancements in precision manufacturing, the proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs), and the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs and competition from alternative gear manufacturing methods like grinding and 3D printing may influence market dynamics.
For more details about the industry, get the PDF sample report for free
Automotive Industry Expansion
The automotive sector remains a significant contributor to the demand for gear hobbing machines. The increasing production of passenger vehicles necessitates high-precision gears for various systems, including steering, braking, and window mechanisms. Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are focusing on expanding into emerging markets like China and India, where motorization is less developed compared to North America and Europe. This expansion drives the need for efficient gear manufacturing solutions.
Surge in Automation and Industry 4.0 Integration
The rise of industrial automation across industries is propelling the adoption of gear hobbing machines. Integration of Industry 4.0 technologies enhances efficiency, connectivity, and data analytics, leading to improved production processes. The shift towards smart manufacturing necessitates advanced machinery capable of producing complex gear designs with high precision.
Growth in Electric Vehicle Production
The automotive industry's transition towards electric vehicles (EVs) is influencing gear manufacturing requirements. EV drivetrains demand lightweight, high-torque gears, prompting the need for specialized gear hobbing machines capable of producing such components. This shift presents opportunities for manufacturers to cater to the evolving demands of the EV market.
Advancements in 3D Printing Technology
The emergence of 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has revolutionized gear production. This technology allows for the creation of intricate geometries that are challenging with traditional methods. While the initial investment in 3D printing equipment can be high, it offers long-term cost savings through material optimization and reduced waste. Industries such as automotive and aerospace are increasingly adopting 3D printing for gear manufacturing.
Shift Towards Vertical Gear Hobbing Machines
Vertical gear hobbing machines are gaining popularity due to their versatility and suitability for small-batch production. These machines offer easy access for loading and unloading parts, occupy less floor space, and are ideal for producing smaller gears required in robotics and electronics applications. The trend towards vertical machines is expected to continue, driven by their efficiency and adaptability.
High Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs
The adoption of advanced gear hobbing machines involves significant capital expenditure, which can be a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Additionally, the need for skilled labor to operate and maintain these machines adds to the overall cost, potentially limiting market entry for smaller players.
Competition from Alternative Gear Manufacturing Methods
Advancements in grinding technology and the adoption of 3D printing are providing alternative methods for gear production. Grinding processes offer improved gear quality and symmetry, while 3D printing enables the manufacturing of complex gear designs with reduced material waste. These alternatives may pose challenges to traditional gear hobbing methods, especially in terms of cost-effectiveness and production efficiency.
See What’s Inside: Access a Free Sample of Our In-Depth Market Research Report
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector is the largest application segment for gear hobbing machines. The increasing demand for precision gear manufacturing equipment to support electric vehicle (EV) drivetrain components has led to a shift towards EVs. The growing requirement for specialized gear machining solutions due to the use of new materials in vehicle manufacture, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, is significantly contributing to the growth of this segment.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector requires high-strength and precise gears capable of withstanding extreme conditions. Investments in this sector are fueling demand for gear hobbing machines capable of producing gears with tight tolerances, thereby offering ample growth opportunities.
Industrial Machinery
The industrial machinery segment benefits from advancements in automation and robotics, driving the need for precision gears in various applications. Gear hobbing machines play a pivotal role in producing gears that cater to stringent tolerance requirements, making them indispensable in manufacturing where accuracy is critical.
Vertical Gear Hobbing Machines
Vertical gear hobbing machines are widely adopted due to their versatility and suitability for small-batch production. They offer easy access for loading and unloading parts, occupy less floor space, and are ideal for producing smaller gears required in robotics and electronics applications.
Horizontal Gear Hobbing Machines
Horizontal gear hobbing machines are known for their efficiency and versatility in handling complex gear components. They are extensively used in automotive and aerospace industries for producing gears with high precision and quality.
The global market is segmented into the following regions:
United States
The U.S. automotive industry has seen a steady increase in production, with light vehicle sales reaching an annualized total of 15.4 million units in the first quarter of 2024, reflecting a 2.7% increase compared to the same period last year. The growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and advancements in automation are driving the demand for gear hobbing machines in the region.
Canada
Canada's automotive sector is experiencing growth, with a focus on precision manufacturing to meet the demands of the evolving automotive industry. The adoption of advanced gear hobbing machines is facilitating the production of high-quality gears for various applications.
China
China is anticipated to play a significant role in the market expansion of gear hobbing machines in the Asia Pacific region. The country's industrial growth, particularly in automotive and aerospace sectors, is driving the demand for precision gear manufacturing solutions.
India
India is witnessing an increase in automotive production, with a total of 25,931,867 vehicles produced from April 2022 to March 2023. This growth is contributing to the rising demand for gear hobbing machines to support the manufacturing of precision gears for various vehicle systems.
Indonesia
Indonesia is emerging as a key player in the Asia Pacific region, with increased industrial activities and investments in the automotive sector, thereby fueling the demand for gear hobbing machines.
Germany
Germany's automotive and industrial machinery sectors are driving the demand for gear hobbing machines. The country's focus on precision engineering and technological advancements is contributing to the growth of the market.
France
France's aerospace industry requires high-strength and precise gears capable of withstanding extreme conditions, thereby increasing the demand for advanced gear hobbing machines.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom's automotive sector is experiencing growth, with a focus on precision manufacturing to meet the demands of the evolving automotive industry.
The Gear Hobbing Machines Market is experiencing robust growth due to increasing demand from the automotive industry, aerospace sector, and industrial machinery producers. The rising popularity of electric vehicles and expanding production of passenger cars has driven the need for precision gears and automotive drivetrain components, thereby boosting gear production and gear manufacturing operations globally. In parallel, the offshore equipment and deepwater drilling sectors, fueled by increased drilling activities, require durable gear systems for critical power transmission applications. Additionally, the shift toward energy-efficient gears in industrial applications is encouraging manufacturers to adopt advanced machine tools and gear cutting solutions. With a growing second-hand market in emerging markets, the accessibility of gear hobbing technology is expanding, further supporting production expansion and cost-effective gear machining across diverse regions.
Request Your Free Report Sample – Uncover Key Trends & Opportunities Today
The gear hobbing machines market is characterized by the presence of several key players implementing various strategies to enhance their market presence. These strategies include product differentiation, market expansion, technological innovation, and strategic partnerships. Notable companies in the market include:
Bourn and Koch Inc.
Brighton Equipment Corp.
Chongqing Machine Tool Co. Ltd.
DMG MORI Co. Ltd.
DVS TECHNOLOGY GROUP
EMAG GmbH and Co. KG
Gleason Corp.
Helios Gear Products
KLINGELNBERG GmbH
Liebherr International Deutschland GmbH
LMT Tools GmbH and Co.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
Monnier and Zahner AG
Premier Gear and Machining Inc.
Reishauer AG
Swegon Group AB
UCAM Pvt. Ltd.
WTO Werkzeug-Einrichtung GmbH
Star SU LLC
On the research front, attention is focused on technological advancements in gear hobbing machines, especially the integration of CNC machines, advanced grinding, and automation surge in industrial automation. The evolution of 3D printing and additive manufacturing is complementing conventional machining processes, enabling greater material efficiency, tool life, and machine stability. Industries are increasingly prioritizing precision engineering to meet stringent gear quality and high precision requirements in both automotive components and aerospace gears. The application of grinding technology in gear finishing ensures surface accuracy, which is critical for achieving efficiency gains and cost reduction. Furthermore, global trends in manufacturing shift—particularly toward smart and flexible manufacturing technology—highlight the role of gear hobbing in adapting to modern industrial needs. This innovation-driven environment continues to position gear hobbing as a cornerstone in advanced manufacturing systems.
Safe and Secure SSL Encrypted