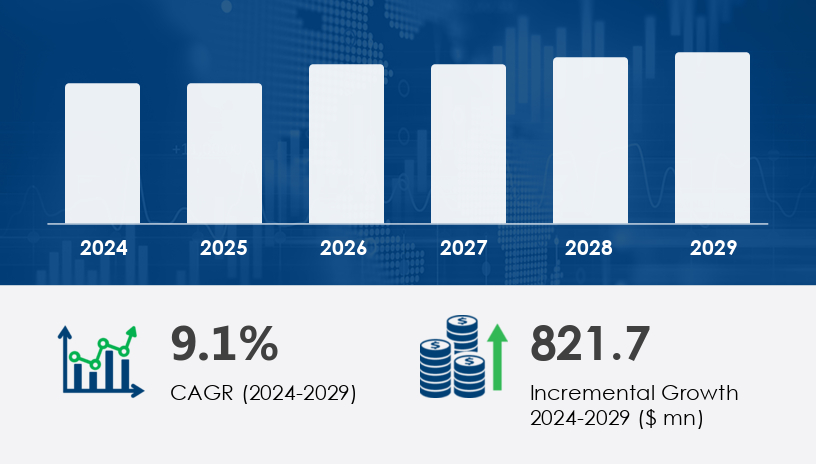
The global small wind turbine market is on the brink of substantial growth, with a projected increase of USD 821.7 billion at a CAGR of 9.1% from 2024 to 2029. This rise signals a turning point for the renewable energy sector, as small wind turbines are becoming a key player in addressing the growing global energy crisis. With governments, private companies, and rural communities increasingly turning to renewable energy solutions, small wind turbines are emerging as a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to conventional power generation.
For more details about the industry, get the PDF sample report for free
The primary driver of growth in the Small Wind Turbine Market is the accelerating investment in renewable energy projects. Countries like India, China, and Japan are deploying billions of dollars into clean energy infrastructure. A notable example includes India’s State Investment Promotion Board (SIPB) approving a ₹246 crore (approximately USD 29.5 million) investment for Greenko’s 4,230 MW renewable energy projects. These capital flows are fostering demand for distributed power generation using small wind turbines, particularly in off-grid and rural applications. Additionally, increased use of tax credits and feed-in tariffs incentivizes wind turbine tower installations, further accelerating market adoption. According to analysts, this trend is central to energy diversification efforts and aligns with long-term sustainability goals.
A leading trend reshaping the Small Wind Turbine Market is the adoption of hybrid energy systems, especially in urban infrastructure. Hybrid street lighting systems, which merge solar panels with small wind turbines and LED lighting, are gaining traction for their efficiency and cost savings. Simultaneously, the market is seeing integration of energy storage solutions—primarily battery systems—to mitigate wind energy intermittency and stabilize output. Technologies like permanent magnet generators and smart grid integration are also enhancing system reliability and efficiency. These advancements, alongside growing public acceptance and regulatory backing for green infrastructure, are expanding the footprint of small wind turbines in residential, commercial, and municipal sectors.
The Small Wind Turbine Market is gaining traction globally due to the growing push for renewable energy, energy independence, and carbon reduction. These turbines, typically installed in remote or localized settings, include both horizontal axis and vertical axis configurations, each suited for different applications. Small turbines are widely used in off-grid power and on-grid power systems, often integrated with hybrid streetlight or solar-wind hybrid solutions to maximize efficiency. The inclusion of battery storage enhances reliability, particularly in areas with fluctuating wind patterns. Core components like the wind rotor, turbine blades, and electrical generator work in harmony with technologies such as the yaw motor and wind anemometer to ensure optimal energy capture. The system’s control system and tower foundation are critical for long-term durability and precise performance, whether the unit functions as an upwind turbine or downwind turbine, depending on wind direction and wind shear conditions.
The Small Wind Turbine Market is segmented as follows:
By Type
Horizontal axis
Vertical axis
By Installation Site
Onshore
Offshore
Among the segments, horizontal axis wind turbines hold the largest share and are expected to continue leading growth through 2029. Valued at USD 748.7 million in 2019, this segment has demonstrated consistent expansion, benefiting from their superior efficiency and commercial viability. Horizontal axis turbines feature a horizontal rotor shaft, which, especially in upwind configurations, offers maximum energy capture. While these systems require mechanisms to adjust blade pitch and yaw, their energy output and ease of integration with smart grids make them ideal for large-scale and community-based installations. Analysts note that their efficiency, proven design, and compatibility with evolving energy standards make them a preferred option across industries.
Covered Regions:
North America (US)
Europe (Germany, UK)
APAC (China, Japan)
Rest of World (ROW)
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is forecast to contribute 49% of global market growth between 2025 and 2029, positioning it as the leading regional market. Countries like China and India are experiencing rapid industrialization and urbanization, driving demand for decentralized and off-grid renewable solutions. Small wind turbines, with minimal ecological disruption and easier land use planning, offer an attractive alternative to large wind farms. Analysts highlight that APAC’s favorable renewable energy policies, such as tax incentives and feed-in tariffs, are enabling broader adoption. In China, for instance, rural electrification initiatives and a focus on low-carbon urban development are reinforcing the role of small wind power systems. As a result, the region is seeing increased investments in turbine design optimization, grid integration, and hybrid systems.
See What’s Inside: Access a Free Sample of Our In-Depth Market Research Report.
Despite positive momentum, the Small Wind Turbine Market faces a significant challenge: price competition from solar photovoltaic (PV) systems. The declining costs of solar PV modules, driven by technological advancements and mass production economies of scale, make solar more accessible in many off-grid applications. Solar systems, often equipped with energy storage, can function independently and require less maintenance than wind turbines. This presents a major hurdle for vertical axis and other small wind designs, which require frequent maintenance, complex blade pitch adjustments, and careful land use planning. Turbine life cycle costs and the need for wind resource assessment further complicate investment returns, making it critical for wind system providers to enhance turbine reliability and reduce operating costs to remain competitive.
Market research reveals increasing deployment of small wind turbines in various applications driven by the need for clean energy, distributed generation, and support for rural electrification. Both residential turbine and commercial turbine segments are expanding, particularly in regions developing microgrid systems to address energy access gaps. Site assessments based on wind resource availability and wind speed data are crucial for project planning. Policy mechanisms like net metering, feed-in tariff, and government-backed tax credits are playing vital roles in driving adoption. Technical improvements, including more responsive blade pitch adjustment and enhanced turbine efficiency, contribute to system viability. Additionally, user demands for low noise, compact design, and durability have pushed manufacturers toward using components like permanent magnet generators and advanced materials that optimize performance while reducing environmental impact.
Deeper research analysis underscores the market’s alignment with broader grid modernization and sustainability goals. Enhancing grid connectivity and integrating energy storage solutions such as batteries and flywheels allow small wind systems to provide stable energy to homes, farms, or institutions. Devices like the power inverter help ensure compatibility with existing electrical systems. While large-scale wind farm developments dominate headlines, small wind turbines play a vital complementary role in decentralized green energy distribution. Their potential contribution to the smart grid is increasingly acknowledged, especially in peak shaving, demand response, and backup power applications. With a focus on sustainability, resilience, and affordability, the small wind turbine market remains a critical pillar in the transition to decentralized, low-carbon energy systems.
To address market dynamics and intensify their footprint, key players are adopting innovative strategies including product launches, strategic alliances, and capacity expansions:
Vestas Wind Systems launched the V117-2.2 MW turbine in 2023, targeting decentralized applications. This innovation is expected to boost Vestas' share in the off-grid small wind segment by offering advanced performance in diverse wind conditions.
In April 2024, Siemens Gamesa and Enel Green Power announced a strategic partnership to co-develop and market small wind turbines in the U.S., signaling strong momentum in North America’s distributed energy landscape.
Nordex SE, backed by a USD 166 million investment in June 2024, plans to scale up small wind turbine production to meet rising demand, particularly in the U.S. market.
Additionally, the European Union’s Renewable Energy Directive II, enacted in October 2025, mandates 15 GW of small wind capacity by 2030, offering a substantial policy-driven boost to the European market.
Companies like Aelius Turbina, Aeolos Wind Energy, SD Wind Energy, and Hi VAWT Technology Corp. are also enhancing their product portfolios with advanced turbine models featuring smart control systems, triple safety mechanisms, and direct drive systems to reduce maintenance overhead.
1. Executive Summary
2. Market Landscape
3. Market Sizing
4. Historic Market Size
5. Five Forces Analysis
6. Market Segmentation
6.1 Type
6.1.1 Horizontal axis
6.1.2 Vertical axis
6.2 Installation Sites
6.2.1 Onshore
6.2.2 Offshore
6.3 Geography
6.3.1 North America
6.3.2 APAC
6.3.3 Europe
6.3.4 ROW
7. Customer Landscape
8. Geographic Landscape
9. Drivers, Challenges, and Trends
10. Company Landscape
11. Company Analysis
12. Appendix
Safe and Secure SSL Encrypted