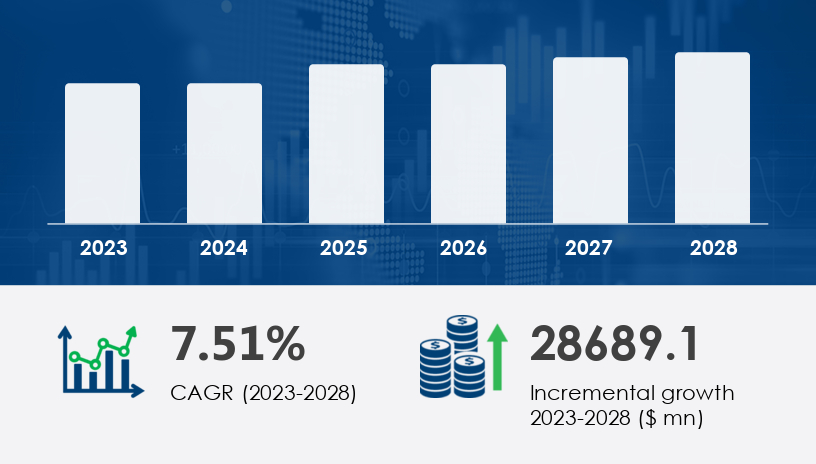
The global Waste to Energy (WtE) market is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by the urgency to reduce environmental pollution, manage surging waste volumes, and transition to renewable energy. Between 2023 and 2028, the market is projected to grow by USD 28.69 billion, registering a CAGR of 7.51%. This growth is fueled by heightened awareness of climate change, increasing municipal and industrial waste generation, and the energy potential of waste materials—particularly organic, municipal solid, agricultural, and industrial waste.
For more details about the industry, get the PDF sample report for free
The Waste to Energy (WTE) Market is undergoing a significant transformation driven by advanced technologies such as incineration technology, gasification process, and pyrolysis reactor. These processes play a pivotal role in converting municipal solid waste, organic waste, and industrial waste into usable energy. Anaerobic digestion and biogas plant facilities are central to biogas production, which supports both clean energy goals and the circular economy model. Alongside, systems like bioethanol production, biomass boilers, and waste shredders are being adopted to optimize waste management efficiency. Thermal energy from steam turbines and heat exchangers enhances the energy recovery process, while innovations such as plasma gasification enable cleaner syngas production. Equipment like waste sorters, flue gas management units, ash collectors, and waste compactors ensures minimal environmental impact through better emissions and residue control.
Top companies are scaling operations through strategic alliances, partnerships, mergers, and project launches, strengthening their footprint globally and in the US:
These key players are pushing innovations in incineration, gasification, and pyrolysis technologies while expanding global and regional energy infrastructure.
See What’s Inside: Access a Free Sample of Our In-Depth Market Research Report.
Europe is forecast to contribute 43% of global market growth through 2028, with advanced WtE infrastructure across:
Germany: Over 80 operational plants, making it the most mature WtE market in Europe.
France
UK
Sweden
Denmark
Netherlands
Europe’s commitment to reducing fossil fuel dependence, coupled with climate legislation, positions the region as a leader in WtE adoption. Technologies such as anaerobic decomposition, incineration, and pyrolysis are widespread, converting biomass and organic waste into biogas and bioethanol.
China: A major contributor to global WtE growth, with significant investment in thermal incineration and waste conversion infrastructure.
Japan: Prioritizes sustainable waste management with strict environmental standards and advanced energy recovery systems.
United States: Witnessing renewed WtE investments through Veolia’s USD 100 million plant launched in January 2025, and Waste Management Inc.’s USD 300 million partnership in December 2024 to develop cutting-edge projects across the region.
Rising urbanization and environmental regulations are pushing interest in WtE technologies, particularly incineration and gasification, in waste-heavy economies.
Adopting WtE solutions to address mounting urban waste and power shortages through efficient waste conversion technologies.
Includes incineration, gasification, and pyrolysis.
Incineration remains the most widely used, converting waste into steam for electricity.
Gasification: Converts waste into syngas in low-oxygen environments.
Pyrolysis: Heats waste in the absence of oxygen to create liquid and gas fuels.
Biomass, derived from organic waste, is a key feedstock.
The thermal segment was valued at USD 43.5 billion in 2018, showing consistent growth through 2028.
Biological Technology
Electricity: Primary output from incineration and gasification-based facilities.
Heat: Captured from combustion or gasification processes and redirected for industrial or municipal heating.
Climate Change Awareness:
Organizations and governments are prioritizing carbon reduction and air quality improvement, pushing the adoption of WtE to cut landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
WtE serves as a renewable alternative to fossil fuels, offering biogas and bioethanol production capabilities while mitigating climate impacts.
Surging Waste Volumes:
Industrialization and urbanization are leading to explosive growth in municipal, industrial, and agricultural waste, demanding scalable energy recovery systems.
WtE solutions are emerging as economically viable and environmentally necessary, providing power while managing waste streams.
Rise in Waste Generation:
The global waste crisis is intensifying, especially in urbanized and rapidly developing regions.
Countries are turning to WtE systems to divert waste from landfills, reduce pollution, and generate renewable energy efficiently.
Biofuels as a Focus Area:
Biogas and bioethanol, generated through anaerobic decomposition, are seeing increasing demand due to their low emissions profile and potential to power electricity grids and transport sectors sustainably.
High Operational and Maintenance Costs:
Thermal WtE facilities demand high upfront investment and sophisticated operational infrastructure.
Costs stem from waste sorting, pre-processing, and multi-step combustion, making them more expensive than conventional disposal.
Additionally, emissions control, labor, and energy input requirements add to the expense, especially in developing markets.
These barriers necessitate policy support, financial incentives, and technology innovation to maintain momentum in adoption.
Request Your Free Report Sample – Uncover Key Trends & Opportunities Today
January 2025 – Veolia launched a USD 100 million WtE plant in the U.S., designed to process 500,000 tons of municipal waste annually, converting it to renewable electricity.
December 2024 – Waste Management Inc. formed a USD 300 million partnership with a global energy company to develop advanced WtE projects across North America, focusing on high-efficiency conversion technologies.
November 2024 – Covanta Energy opened a USD 250 million facility in Europe, utilizing state-of-the-art incineration to supply clean energy to local industries and communities.
October 2024 – Babcock & Wilcox secured a USD 150 million contract to deliver waste-to-energy systems in Asia, converting municipal waste into steam and electricity.
In-depth analysis of the WTE market highlights the integration of emerging technologies such as biofuel generators and thermal converters, which support advanced energy conversion systems. The incorporation of carbon capture and methane capture technologies is also rising, significantly contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Projects focusing on renewable energy are increasingly leveraging landfill gas and waste pretreatment techniques to maximize the calorific value of the waste stream. Methods of biological conversion and thermal treatment are also being explored to improve energy efficiency in power generation from agricultural waste. Furthermore, advancements in combustion processes, waste sorting, and waste recycling support long-term waste disposal strategies and ensure a sustainable approach to handling the growing volume of waste globally. These innovations collectively shape a future where energy production and waste reduction work hand in hand.
Safe and Secure SSL Encrypted