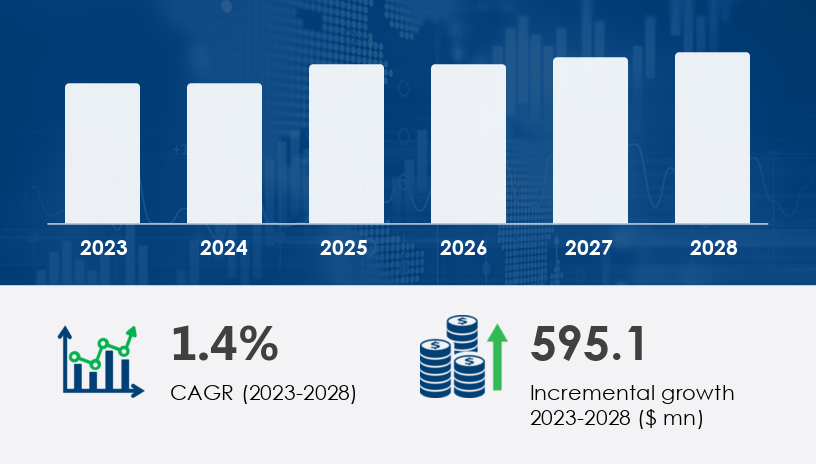
Hydraulic elevators market is projected to expand by USD 595.1 million from 2023 to 2028, growing at a CAGR of 1.4%, according to recent market research. This upward trajectory is largely powered by cost-effective installation advantages and innovations like Hydraulic Infinite Linear Actuator (HILA) systems that promise smoother, safer, and more energy-efficient vertical transportation. In this 2025 Outlook, we provide a comprehensive guide to the key growth drivers, evolving market segments, and strategic opportunities shaping the global hydraulic elevators landscape.For more details about the industry, get the PDF sample report for free
Hydraulic elevators are vertical transportation systems that use a hydraulic fluid-based mechanism involving pistons, cylinders, and electronic pumps to move elevator cabs vertically. Unlike traction elevators, they don’t require an overhead machine room, making them space-saving and ideal for low-rise buildings — particularly in commercial and residential structures
Hole-less Hydraulic Elevators (Fastest Growing)
No need for drilled holes
Ideal for low-rise buildings
Above-ground installation minimizes oil contamination
Supported by telescopic cylinders and twinpost jacks
Holed Hydraulic Elevators
Traditional systems using in-ground jacks
Require more space and drilling infrastructure
Roped Hydraulic Elevators
Combine hydraulic power with ropes for extended reach
Suited for mid-rise buildings
Case Example: A mid-sized hospital in Delhi replaced its old rope-and-pulley elevators with hole-less hydraulic systems. Result? A 15% reduction in maintenance costs and smoother mobility for patients and staff across six floors
APAC (Asia-Pacific):
Accounts for 45% of market growth. China and India are leading, driven by urbanization and government infrastructure initiatives. With 63% of Asia's population living in urban areas, vertical mobility is no longer optional — it's essential.
North America (U.S.):
Mature market focused on energy-efficient upgrades in aging buildings.
Europe (Germany, UK):
Adoption is driven by sustainability compliance and modernization mandates.
Middle East & Africa, South America:
Emerging demand, especially in sectors like logistics and healthcare infrastructure.
Get more details by ordering the complete report
Hydraulic elevators typically require fewer structural modifications, avoiding the costly overhead machine room required by traction systems. Their components — cylinders, pistons, jack modules — are all installed at the shaft base, simplifying setup.
Use of hydraulic fluid allows for inert, controlled lifting
Electronic pumps can recapture heat for secondary uses like space or water heating
New designs integrate jack safety valves and compressors for optimized reliability
A cutting-edge development that merges the stability of hydraulic lifts with the precision of traction elevators. Developed by Linkoping University and SAAB AB, HILA introduces a two-stroke cylinder system for smooth, efficient travel.
“HILA is a hybrid technology that could redefine how we look at energy efficiency and safety in elevator systems,” remarks Senior Technavio Expert.
The rise of machine room-less designs aligns with global preferences for space-saving solutions, particularly in urban settings where every square meter counts.
Pneumatic and traction-based MRL elevators are gaining market share due to:
Higher energy efficiency
Greater reach in high-rise buildings
Lower operating noise levels
Hydraulic systems operate under extreme pressure. Poor maintenance can lead to severe injuries, such as skin punctures or system failure.
For more details about the industry, get the PDF sample report for free
The hydraulic elevators market is experiencing steady growth driven by increasing demand for low-rise, mid-rise, and high-rise elevators across residential, commercial, and industrial segments. Among the major types, hydraulic elevators—including hole-less, holed, and roped elevators—remain prominent due to their cost-effectiveness and simple elevator installation processes. Key components such as the hydraulic piston, hydraulic pump, hydraulic ram, and hydraulic fluid work in tandem to power the elevator car within a dedicated elevator shaft. The evolution of smart elevators and energy-efficient elevators is enhancing elevator efficiency, while improvements in elevator accessibility—including wheelchair lifts—are addressing inclusivity in public and private infrastructure. Emerging trends in elevator design are also influencing the deployment of passenger elevators, freight elevators, and automotive elevators across facilities like malls, hospitals, and parking structures. Moreover, specialized solutions like airport elevators are gaining traction with a growing focus on customized mobility solutions
Developers & Builders:
Opt for hole-less hydraulic elevators in low-rise commercial projects to maximize ROI and reduce long-term costs.
Facility Managers:
Focus on preventive maintenance and system upgrades, especially incorporating electronic pumps and jack modules for energy savings.
Manufacturers:
Invest in R&D for HILA systems and hybrid models to maintain competitive positioning against MRL traction systems.
Capitalize on APAC Expansion:
Prioritize partnerships or distribution in India and China, where infrastructure spending is booming.
Promote Energy Efficiency:
Highlight hydraulic elevators’ ability to generate heat for building utilities in marketing and sales conversations.
Offer Retrofit Solutions:
Develop modular upgrades for older hydraulic systems to improve safety and energy use without full replacements.
Get more details by ordering the complete report
Advanced research in the hydraulic elevators sector underscores rapid innovations in elevator technology, especially in areas like touchless elevators, IoT elevators, cloud monitoring, and voice control. These smart technologies not only enhance user convenience but also support predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and repair costs. Integration of regenerative braking and variable-frequency drives contributes to the rise of eco-friendly elevators, significantly lowering energy consumption. In contrast to traction elevators, modern hydraulic systems offer simplified elevator controls tailored for elevator modernization in existing buildings. Regular elevator maintenance and rigorous safety inspections ensure compliance with regulatory standards and reinforce elevator safety, which remains a core concern for operators and manufacturers. The market’s focus on sustainable growth is matched by rising consumer expectations for high-performance mobility systems, signaling a shift towards more intelligent and resilient hydraulic elevator infrastructure.
Despite the increasing preference for traction and MRL systems, hydraulic elevators retain a strategic niche due to their cost-effectiveness, safety, and durability. With innovations like HILA, hole-less designs, and eco-conscious compressors, hydraulic elevators are adapting to the future. Their role in urban low-rise infrastructure, particularly in emerging markets, ensures they will remain vital players in the global vertical mobility market.
For more details about the industry, get the PDF sample report for free
Safe and Secure SSL Encrypted