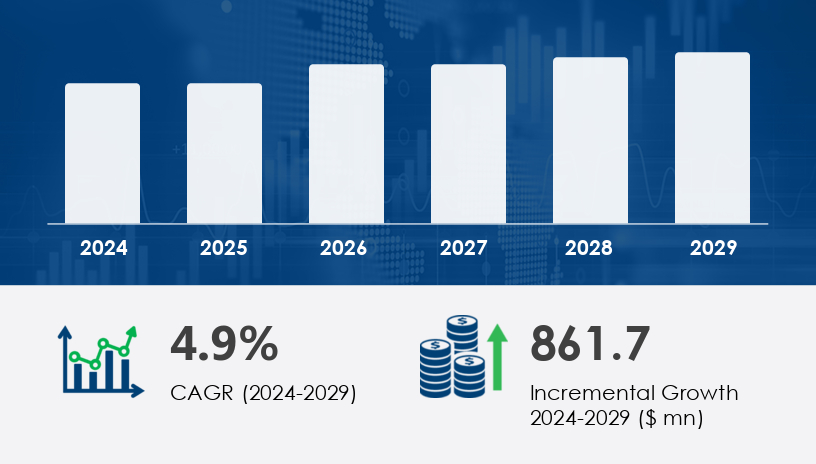
The Arc Welding Robots Market is poised for notable expansion, driven by the surge in industrial automation and technological innovation across the manufacturing sector. In 2024, the market stood at a robust baseline and is forecast to increase by USD 861.7 million by 2029, advancing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.9% over the forecast period.
For more details about the industry, get the PDF sample report for free
A primary driver fueling growth in the Arc Welding Robots Market is the growing popularity of industrial robots across the Asia Pacific (APAC) region. This trend is being propelled by the rapid industrialization of emerging economies and their increasing investments in smart manufacturing. Countries such as China, South Korea, and Japan are leading this transformation, with others like Vietnam and Malaysia rapidly adopting robotics to optimize labor efficiency and meet production demands. These robots are being embraced across industries for their ability to offer precision, repeatability, and consistent performance—particularly vital in high-volume manufacturing environments. This regional trend presents a lucrative opportunity for robot manufacturers to expand their market presence.
One of the most impactful trends in the Arc Welding Robots Market is the adoption of innovative business models, particularly the robot-as-a-service (RaaS) model. This rental-based approach allows manufacturers to integrate robotic welding systems without incurring hefty upfront capital costs. Companies like Hirebotics, Tokyo Century, and ORIX are offering monthly rental plans ranging from USD 1,300 to USD 1,800, including installation, maintenance, and programming services. These models lower the barriers to entry, making advanced automation more accessible to small and mid-sized enterprises. The flexibility, combined with the ability to scale operations, is positioning RaaS as a strategic enabler in the manufacturing ecosystem.
The Arc Welding Robots Market is a key segment within industrial automation, driven by the demand for improved welding precision, welding repeatability, and enhanced manufacturing efficiency. Core applications include robotic welding processes like TIG welding, MIG welding, and SMAW robots, which are widely adopted in sectors such as automotive manufacturing, metal fabrication, and the shipbuilding industry. These robots offer consistent weld quality, even in high-volume environments such as component manufacturing and industrial machinery production. Increasing adoption in the transportation industry reflects the need for scalable and cost-effective solutions, especially where aluminum welding, copper alloys, and nickel welding are involved. With growing robot deployment, there’s also rising interest in collaborative robots, capable of working safely alongside human operators. Advanced integration of vision systems, sensor integration, and robot peripherals enables high-speed welding and superior welding consistency across complex operations.
Segmentation Categories:
By Product
Consumable method
Non-consumable method
By Application
Automotive
Electricals and Electronics
Aerospace and Defense
Others
By Type
Greater than 150 kilograms
50–150 kilograms
Among the product segments, the consumable method leads in terms of market share and growth. In 2019, it was valued at USD 2.05 billion, and it has maintained steady growth since then. This segment is favored in high-speed, high-precision environments such as automotive manufacturing, construction, and general metal fabrication. Processes like Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding, which use consumable wire electrodes, are widely used due to their efficiency and strong weld quality. Analysts note that this segment's dominance is supported by its suitability for high-volume production and adaptability across varied industries.
Covered Regions:
North America
Europe
APAC
South America
Middle East and Africa
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region is the dominant contributor, projected to account for 67% of global market growth during 2025–2029. This strong performance is attributed to government-backed industrial automation initiatives and the rising demand for regionally produced automobiles. Major manufacturing hubs like India and China are deploying arc welding robots to increase throughput and reduce manufacturing cycle times. Additionally, the aerospace and defense sectors are thriving, with Singapore and Malaysia emerging as key maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) centers. According to market analysts, APAC's robust infrastructure development and skilled labor force are critical factors driving the regional adoption of welding automation technologies.
See What’s Inside: Access a Free Sample of Our In-Depth Market Research Report.
Despite the promising outlook, the Arc Welding Robots Market faces significant operational challenges. Chief among them is the complexity of installation and programming, especially for tasks requiring high flexibility. For instance, welding operations involving irregular gaps below 1 mm or parts with narrow access points often necessitate manual intervention, as robotic systems may struggle with variability and precision. These technical limitations reduce the applicability of welding robots in low-volume or highly customized production settings. Furthermore, the high upfront investment costs deter adoption, particularly among small manufacturers in emerging markets. These challenges underscore the need for more adaptive and user-friendly robotic solutions.
The market's growth is further propelled by innovations in advanced robotics and the adoption of automation technology that supports scalable deployment. Companies are leveraging cloud robotics, real-time monitoring, and big data to enhance welding performance and improve production rates. The role of predictive maintenance and cyber-physical systems is becoming central to minimizing downtime and ensuring system longevity. Integration with IIoT adoption also enables smarter operations through connected infrastructure. Support services are essential to deployment, with offerings like programming support, maintenance services, and flexible leasing options from providers such as Tokyo Century, ORIX rentals, and rental companies. Emerging platforms like Hirebotics solutions are reshaping access by offering robots-as-a-service (RaaS) models, while demand for welding consistency and welding performance remains high. Research shows that welding repeatability and real-time adaptability are key metrics manufacturers track when optimizing workflows with robotic systems.
Research analysis reveals a steady shift toward intelligent and autonomous arc welding systems that align with the future of smart manufacturing. Market trends highlight the increasing importance of software-driven control, AI-based optimization, and seamless human-machine collaboration. Manufacturers focusing on sustainable production, precision, and lower operational costs are driving demand for integrated welding robots that deliver reliable performance across a range of industrial applications.
Innovations and Recent Developments
To stay competitive, key players are investing in technological innovation and strategic acquisitions. For instance, leading manufacturers are enhancing robot capabilities through integrated vision systems, real-time data analytics, and zero-downtime automation. These innovations improve weld accuracy and production efficiency, making them ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace manufacturing.
Additionally, companies are expanding their reach through geographical expansion and partnerships. Businesses like ABB Ltd., FANUC Corp., Panasonic Holdings Corp., and Yaskawa Electric Corp. are leveraging mergers and acquisitions to broaden their technology portfolio and customer base. Strategic alliances also enable companies to offer bundled solutions that include programming support, system analysis, and maintenance services—addressing end-user concerns around complexity and cost.
According to analysts, the competitive landscape is evolving, with companies increasingly categorized based on specialization: pure play, category-focused, industry-focused, or diversified. Market leaders are those that provide holistic, scalable, and industry-specific solutions, ensuring that clients benefit from tailored automation strategies.
1. Executive Summary
2. Market Landscape
3. Market Sizing
4. Historic Market Size
5. Five Forces Analysis
6. Market Segmentation
6.1 Product
6.1.1 Consumable method
6.1.2 Non consumable method
6.2 Application
6.2.1 Automotive
6.2.2 Electricals and electronics
6.2.3 Aerospace and defense
6.2.4 Others
6.3 Type
6.3.1 Greater than150 kilograms
6.3.2 50-150 kilograms
6.4 Geography
6.4.1 North America
6.4.2 APAC
6.4.3 Europe
6.4.4 South America
6.4.5 Middle East And Africa
7. Customer Landscape
8. Geographic Landscape
9. Drivers, Challenges, and Trends
10. Company Landscape
11. Company Analysis
12. Appendix
Safe and Secure SSL Encrypted